
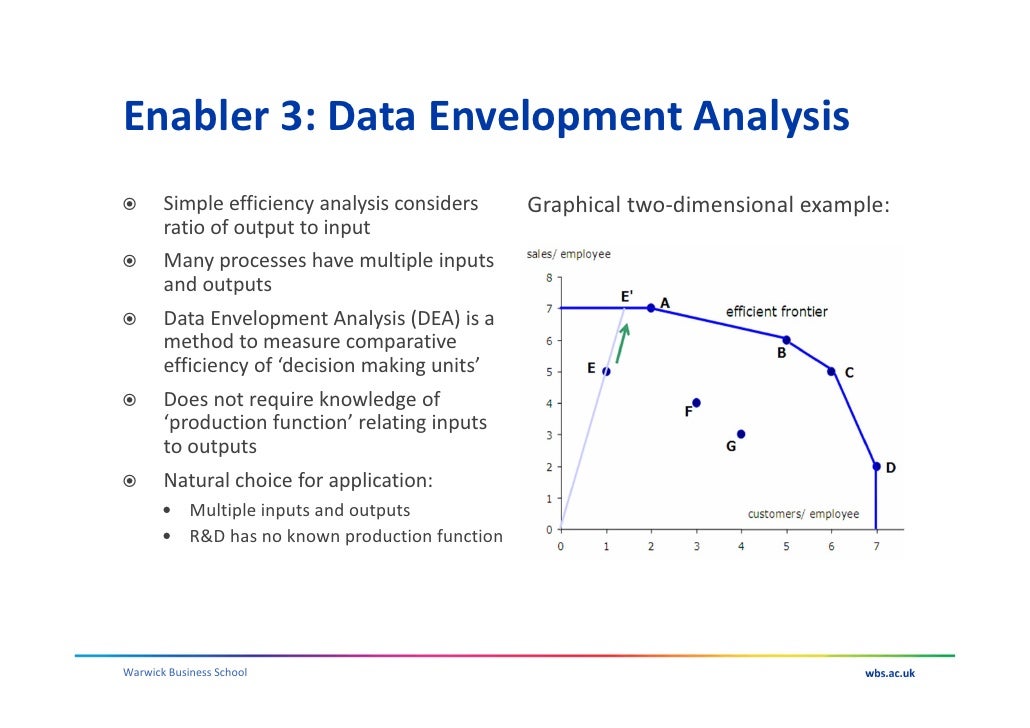
In the present paper, a new separate variable is introduced which makes it possible to determine whether operations were conducted in regions of increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale (in multiple input and multiple output situations). Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) which shows either constant returns to scale (CRS) or variable returns to scale (VRS) on the basis of the equality of the input-output. Methods for identifying and correcting the magnitudes of these inefficiencies, as supplied in prior work, are illustrated. Technical inefficiencies are identified with failures to achieve best possible output levels and/or usage of excessive amounts of inputs. A separation into technical and scale efficiencies is accomplished by the methods developed in this paper without altering the latter conditions for use of DEA directly on observational data. Data envelopment analysis is a non-parametric linear programming-based technique used for measuring the relative performance of organizational units where the presence of multiple inputs and outputs makes comparisons difficult. Given a set of input factors, and a set of output factors, for each decision making unit (DMU), i, find a set of weights for the factors so as to maximize efficiency score of i (wgted outputs)/(wgted inputs). Simulations are also performed using Microsoft Excel Solver as it required simple linear. Data Envelopment Analysis of Decision Maker Efficiency. The CCR ratio form introduced by Charnes, Cooper and Rhodes, as part of their Data Envelopment Analysis approach, comprehends both technical and scale inefficiencies via the optimal value of the ratio form, as obtained directly from the data without requiring a priori specification of weights and/or explicit delineation of assumed functional forms of relations between inputs and outputs. (1978) proposed Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) to assess the. Mathematical programming is thereby extended for use as a tool for control and evaluation of past accomplishments as well as a tool to aid in planning future activities. Data Envelopment Analysis reverses this role and employs mathematical programming to obtain ex post facto evaluations of the relative efficiency of management accomplishments, however they may have been planned or executed. sampling and regression Operational research and strategy Data envelopment analysis.

A list of available DEA models is in picture at the left side of this page. There are three versions available - free, academic and commercial. In this capacity, mathematical programming serves as a planning aid to management. Data analysis Data management Data science Data visualisation. Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) DEAFrontier (TM) developed by Professor Joe Zhu is a Microsoft® Excel Add-In for solving Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) models. In management contexts, mathematical programming is usually used to evaluate a collection of possible alternative courses of action en route to selecting one which is best. Network data envelopment analysis (DEA) concerns using the DEA technique to measure the relative efficiency of a system, taking into account its internal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
